Bikecast: Demand Forecasting
A machine learning-powered service addressing bike shortages in Seoul's "Ddareungi" system. Uses XGBoost to predict demand and recommend new station locations.
Project Overview
Bikecast analyzes over 44 million trip records from Seoul's public bike system to solve supply/demand imbalances. By correlating weather, public transit usage, and elevation data, it provides actionable insights for bike redistribution and station planning.
Key Engineering Contributions
Big Data Infrastructure
Engineered the MySQL database schema to efficiently handle 44M+ trip records. Implemented advanced indexing strategies that reduced complex query retrieval times from hours to tens of seconds (99% reduction).
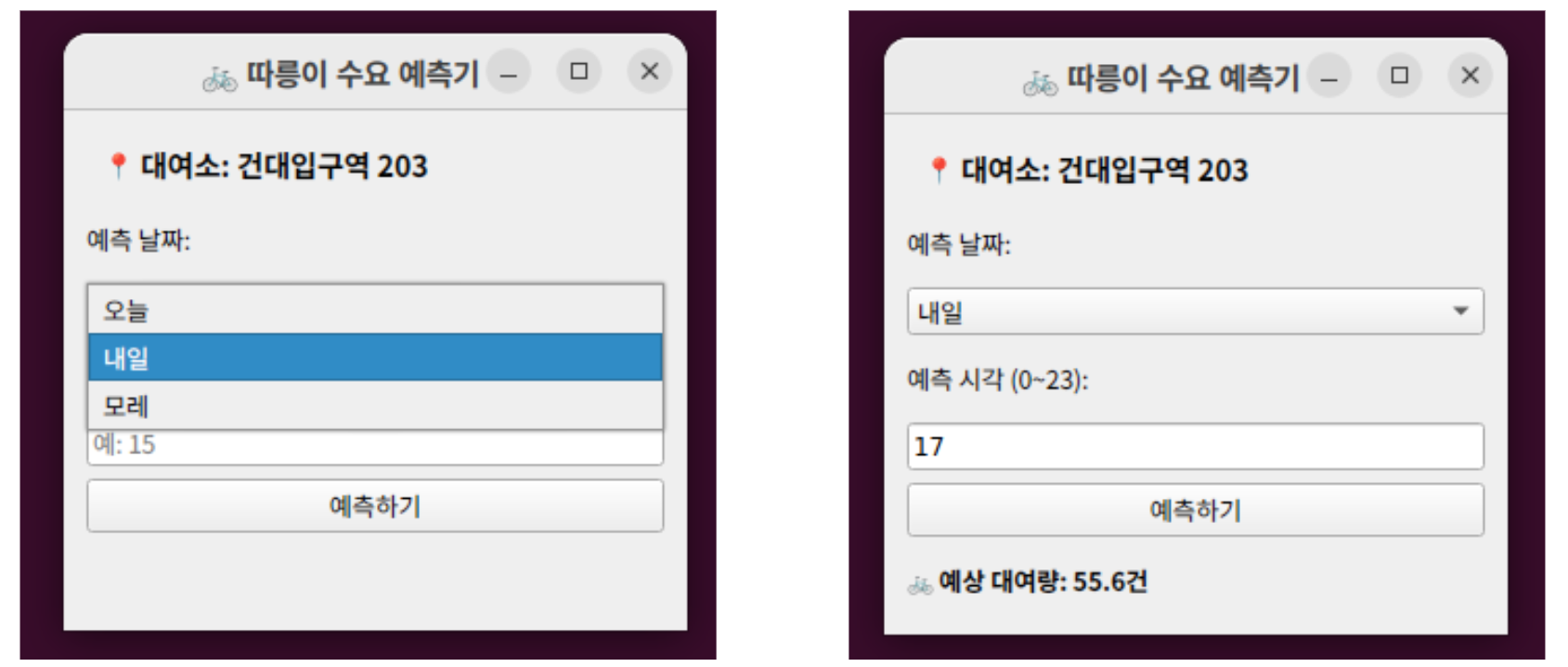
Demand Forecasting Model (SR_01)
Developed the core XGBoost regression model to predict station-level hourly demand. Feature engineering included creating composite variables for weather impact, seasonality, and proximity to transit hubs, achieving an R² of 0.835.
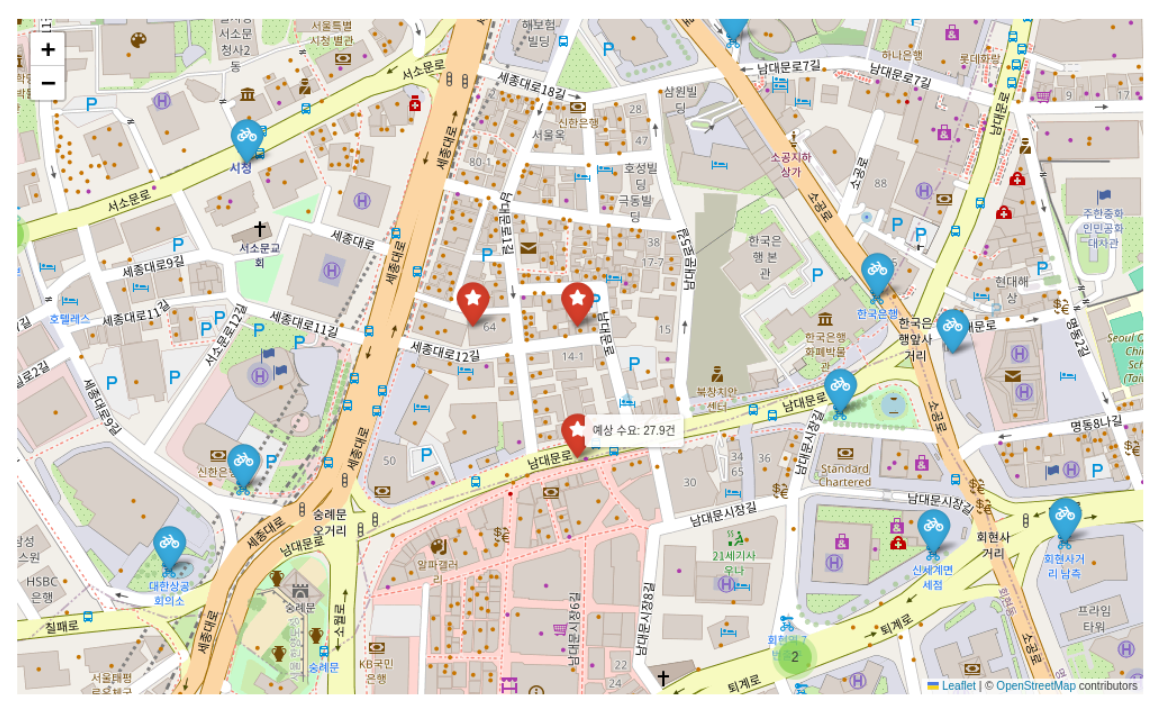
Site Recommendation Engine (SR_02)
Implemented the Site Recommendation logic that analyzes spatial correlations. The algorithm identifies "underserved" high-potential areas by cross-referencing population density, subway exits, and existing station overflow patterns.
Key Analysis Findings
- Commute Patterns: Clear demand peaks observed at 7-9 AM and 5-7 PM.
- Weather Impact: Optimal riding temperature identified around 22°C. Precipitation significantly drops usage.
- Location Factors: Lower elevation and proximity to transit hubs strongly correlate with higher turnover rates.
Tech Stack
Technical Challenges & Evaluation
Problem: Handling 44 million rows locally was inefficient.
Solution: Migrated to AWS RDS with optimized indexing strategies to enable
real-time analysis capabilities.
Observation: While effective for general trends, the model struggles with non-linear spikes in ultra-high demand areas due to external factors not captured in public data (e.g., local events).